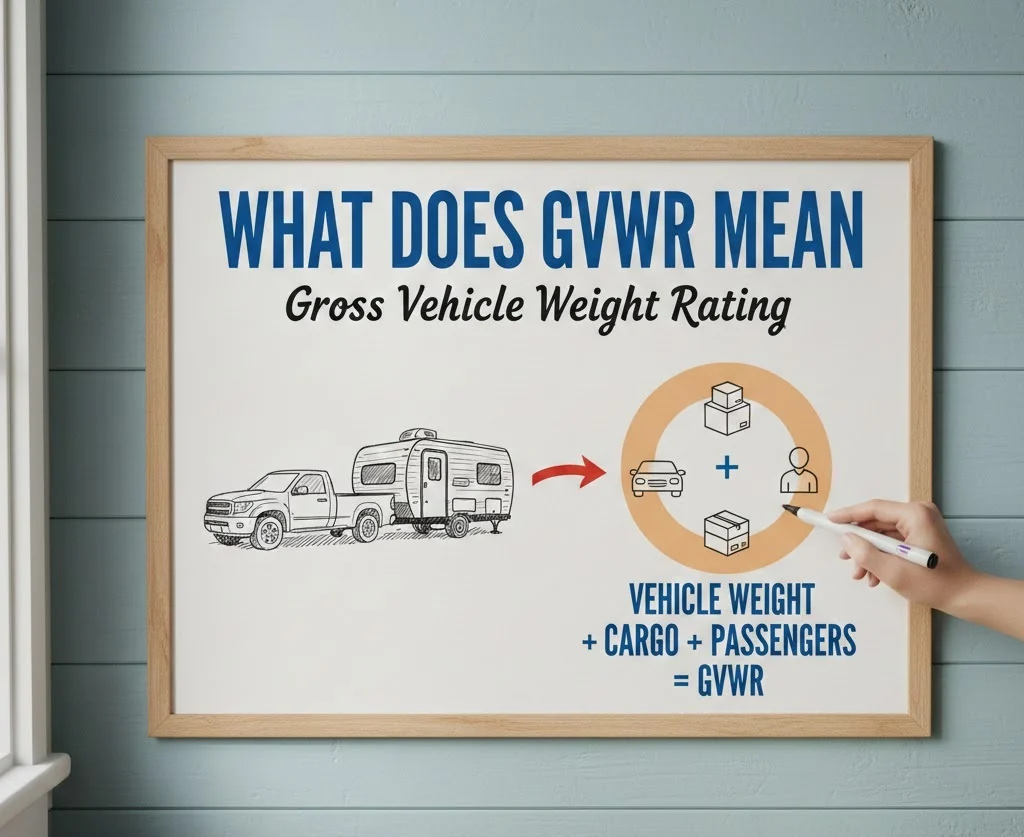
If you’ve ever checked your vehicle’s specifications or shopping for a new truck, SUV, or van, you might have seen the acronym GVWR. But what does GVWR mean, and why does it matter?
GVWR stands for Gross Vehicle Weight Rating—a key number that tells you the maximum safe weight your vehicle can carry, including passengers, cargo, and fuel. Ignoring GVWR can lead to mechanical problems, accidents, or legal issues.
Whether you’re a first-time vehicle owner, a truck enthusiast, or a professional driver, understanding GVWR is essential. In this guide, we’ll cover everything from definitions, practical examples, historical background, safety tips, and professional guidance to ensure you drive safely and legally.
Definition & Meaning of GVWR
GVWR, or Gross Vehicle Weight Rating, is the maximum weight a vehicle is rated to carry safely. This includes:
- Vehicle weight (the car, truck, or SUV itself)
- Passengers
- Cargo and luggage
- Fuel
Key Points:
- Exceeding GVWR can strain suspension, brakes, and tires.
- GVWR is different from curb weight, which is the vehicle’s weight without passengers or cargo.
- GVWR is legally required to be listed on the vehicle’s safety label, usually inside the driver’s side door frame.
Examples in Real Life:
Truck Example:
A pickup truck has a GVWR of 7,000 lbs. The truck itself weighs 5,000 lbs, leaving 2,000 lbs for passengers and cargo.
SUV Example:
SUV GVWR: 6,000 lbs. You have three passengers totaling 450 lbs. Maximum cargo = 1,550 lbs.
Background & History of GVWR
The concept of GVWR originated to enhance vehicle safety and standardize weight limits. Over the years:
- Early automotive era: No standardized limits led to frequent brake failures and accidents.
- 1940s–1970s: Governments introduced weight regulations for trucks and commercial vehicles.
- Modern vehicles: GVWR became mandatory for all new vehicles, helping drivers avoid overloading and improving road safety.
Regional and Regulatory Influence:
- United States: National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) sets GVWR standards.
- Europe: EU regulations enforce similar vehicle weight safety limits.
How GVWR Differs from Other Vehicle Weight Terms
| Term | Meaning | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Curb Weight | Vehicle weight without passengers/cargo | Often used for fuel economy calculations |
| Gross Axle Weight Rating (GAWR) | Maximum weight per axle | Important for trucks and trailers |
| Payload | Maximum weight vehicle can carry (passengers + cargo) | GVWR – Curb Weight = Payload |
| Gross Combination Weight Rating (GCWR) | Max weight with trailer attached | Used for towing |
Key takeaway: GVWR is the umbrella number that determines your vehicle’s maximum safe total weight.
Why GVWR Is Important
Understanding GVWR is critical for vehicle safety and performance:
- Safety: Prevents brake failures, tire blowouts, and suspension damage.
- Legal compliance: Overloaded vehicles may violate state or federal laws.
- Insurance: Insurance claims may be denied if accidents involve overloaded vehicles.
- Performance: Overloading reduces acceleration, fuel efficiency, and handling.
Practical Tip: Always check GVWR before loading heavy cargo or towing a trailer.
How to Find GVWR
GVWR can usually be found in multiple places:
- Driver’s Side Door Jamb: Most common location.
- Owner’s Manual: Manufacturer specifies exact GVWR.
- Vehicle Registration: Some states include weight ratings.
- Manufacturer’s Website: Lookup by make, model, and year.
Example:
2023 Ford F-150: GVWR = 7,000 lbs (check driver’s door label for confirmation).
GVWR in Different Vehicle Types
Cars & SUVs
- GVWR varies based on model and engine size.
- Typical range: 4,000–7,000 lbs.
Pickup Trucks
- Heavier trucks have higher GVWR, often 7,000–14,000 lbs.
Vans & Commercial Vehicles
- GVWR can exceed 15,000 lbs for commercial vans.
Trailers
- GVWR applies to trailers too, crucial for towing safely.
Tip: Always check trailer GVWR and make sure your towing vehicle can handle it.
How GVWR Affects Driving & Safety
Exceeding GVWR can lead to:
- Brake failure
- Poor handling and steering
- Increased stopping distances
- Tire blowouts
Example Scenario:
Overloaded van carrying 3,000 lbs extra cargo beyond GVWR could experience front suspension failure and tire blowouts on highways.
Safety Tip: Use scales at truck stops to check weight if unsure.
GVWR in Professional & Commercial Use
Professional drivers and fleet managers must prioritize GVWR:
- Compliance avoids fines and penalties.
- Proper weight distribution ensures vehicle longevity.
- Fleet software often tracks cargo weight and GVWR.
Pro Tip: For delivery trucks, ensure payload + passengers ≤ GVWR at all times.
GVWR vs Towing Capacity
| Term | Meaning | Difference from GVWR |
|---|---|---|
| GVWR | Max vehicle weight including cargo/passengers | Base vehicle + payload |
| Towing Capacity | Max weight vehicle can tow | Separate from GVWR, depends on hitch and transmission |
Example:
Truck GVWR = 8,000 lbs, Payload = 2,000 lbs, Towing capacity = 5,000 lbs.
Tips for Using GVWR Safely
- Check before loading cargo.
- Balance weight evenly across axles.
- Don’t overload. Always stay under the GVWR.
- Regular maintenance for brakes, tires, and suspension.
- Document payload for commercial vehicles.
Regional & Legal Differences
- US: GVWR defined by NHTSA; violations can incur fines.
- Canada: Provinces have weight enforcement; commercial vehicles strictly monitored.
- Europe: GVWR regulated by EU safety standards.
Tip: International travelers must check local GVWR regulations before driving commercial vehicles abroad.
Common Myths About GVWR
- Myth: GVWR includes only cargo.
Fact: It includes passengers, fuel, and cargo. - Myth: GVWR = towing capacity.
Fact: Towing capacity is separate; GVWR only measures vehicle + payload. - Myth: Slightly exceeding GVWR is safe.
Fact: Even minor overloads affect braking and handling.
FAQs About GVWR
Q1: Can I exceed GVWR for a short trip?
A: No, even minor overloads can be unsafe.
Q2: Does GVWR change with aftermarket modifications?
A: Yes, modifications like lift kits or heavy-duty parts can affect GVWR.
Q3: Where is GVWR listed on my vehicle?
A: Driver’s side door jamb, owner’s manual, or manufacturer label.
Q4: How is GVWR calculated?
A: Vehicle weight + maximum payload capacity = GVWR.
Q5: What happens if I overload my vehicle?
A: Risk of brake failure, suspension damage, tire blowouts, and legal fines.
Q6: Does GVWR affect insurance?
A: Yes, accidents with overloaded vehicles may lead to claim denial.
Conclusion
Understanding what GVWR means is essential for vehicle safety, performance, and legal compliance. It defines the maximum safe weight your vehicle can carry, including passengers, cargo, and fuel. Ignoring GVWR can lead to mechanical failures, accidents, and insurance issues. Whether you drive a car, SUV, truck, or commercial van, always check the GVWR before loading or towing. By following weight limits and maintaining your vehicle, you can ensure safer drives, longer vehicle life, and peace of mind. Keep GVWR in mind every time you travel—safety starts with knowing your limits.
Discover More:-
- What Does a Yellow Ribbon Mean: Symbolism, History & Usage
- What Does Pineapple Mean: Meaning, Usage & Examples
- What Does It Mean When Your Nose Itches: Causes, Superstitions & Health